EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)
is a web service inside AWS infrastructure, which is capable of providing us
Virtual Servers and these virtual serves inside cloud are known as instances.
EC2 enables us to launch and manage server instances at any time, for as long
as we need and for any legal purpose. By default, EC2 is not redundant. Ec2 is
AZ specific service. EC2 cannot be used for hosting Desktop. For this there is
a different application named VDI in AWS.
Q. What is the difference
between S3 web service and EC2 web service?
A. S3 is a web service which
provides 'object storage' whereas EC2 is a web service which provides 'Virtual
Servers'.
Q. If we can get Hardware
Server and Virtual Machine, then why we go for an EC2 instance?
A. Cost and
Flexibility (in terms of size, location,
moving instances) are two main features to move towards the instance
apart from buy a server. Cloud is providing same thing in much more cost
effective mechanism and vast flexibility. In future we can resize the instance
also.
In AWS, Cost matters on below mentioned three things:
- Tenancy Model (Cost Saving Part)
- Billing Model (Cost Saving Part)
- Instance Type (Flexibility Part)
1. TENANCY MODEL
Tenancy Model helps us to control the cost, as we are the tenant
for AWS.
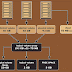
Types of Tenancy Model:
- Shared Tenancy (default)
- Dedicated Tenancy
- Instance
- Host
1. SHARED TENANCY MODEL (e.g. to test our website code):
Shared Tenancy is the default tenancy
model, used by AWS. In Shared Tenancy, our instance can be placed on any
hardware in AWS. Many companies can share their servers on the same hardware.
AWS has hardware and a hypervisor
layer over that hardware. If a company (e.g TCS) wants to create its
instance, EC2 will allow to create the instance on top of the Hypervisor layer.
Secondly, another company (e.g. HCL) wants to launch their instance, then EC2
will allow them also to launch an instance on top of that Hypervisor. This is
Shared Tenancy Model, which is the default tenancy model in AWS.
DISADVANTAGE: If a company
is very sensitive about security or about the government rules and regulations,
in this case, Shared Tenancy Model will not work because these types of
companies will not like another company to share their hardware. Here,
Dedicated Model comes into the picture.
2. DEDICATED TENANCY MODEL:
In Dedicated Tenancy Model, Physical
Server will be dedicated to us to create an instance for our company. In this case, only our company’s instance will run ON THE BLOCK OF THAT HARDWARE. Here, we
are getting ensured by the AWS that, that particular block on which our
instance is running, no other company's instance will be started. AWS is giving
proper SLA for the same.
Q. Who is providing security-related assurance in AWS?
A. Security in AWS is taking care of by PCI (Payment Card
Industry) and DSS (Data Standard Security).
Q. What is the difference between Shared Tenancy Model
and Dedicated Tenancy Model?
A. In Shared Tenancy Model, n number
of companies instances can be started on the same hardware but in Dedicated Tenancy
Model, only our company's instance will be run on that particular hardware.
DISADVANTAGE OF DEDICATED
TENANCY MODEL:
If we reboot our instance, only
OS service restarts. So after reboot, we will be on the same hardware. But if
we perform 'stop and start' activity, it means our instance is fully stopped and
our connection with the hardware is fully disconnected. So, there is no guarantee
that when we start our instance, it will start on the same hardware.
There are two types of Dedicated Tenancy Model:
(i) DEDICATED INSTANCE (e.g. to do data encryption on
medical records):
In this case, EC2 will pick up the keyword that this person
is using Dedicated Tenancy, then EC2 finds the location where our instance can
run as a Dedicated Instance. We use Dedicated
Instance for compliance, security and company policy.
ISSUE: In this case also, if we stop and then start
again our instance, then EC2 can start our instance on other hardware also.
We will get the instance, access, and all settings but hardware may be changed
from one system to another system. But if we reboot the system, then we can get
our instance on the same system. We need to pay more than Shared Tenancy.
(ii) DEDICATED HOST (e.g. to run Cad Cam software):
In this case, complete hardware of the physical server is dedicated to us. Here, we need to pay the entire cost of the physical server, whether we create one instance or use full hardware. We go for Dedicated Host if we want to have a license for our hardware.
In this case, complete hardware of the physical server is dedicated to us. Here, we need to pay the entire cost of the physical server, whether we create one instance or use full hardware. We go for Dedicated Host if we want to have a license for our hardware.
AWS will provide hardware + Bring your own license
SCHEDULER SERVICE:
The moment we make any request, the scheduler knows everything about the infrastructure, also it has a database, based on that it will make a request to place the instance on specific hardware. Scheduler exist inside EC2 service of AWS.
Scheduler first checks on which tenancy we are working, then
it will check how much hardware resource is free and according to that this
will launch the instance.
DISADVANTAGES OF DEDICATED HOST:
- Cost effectively
- In this case, If the host fails then the server will also be fail
- We have reserved hardware to us but we all remaining resources are useless and we have to pay.
2. BILLING MODEL
There are three types of billing options:
- On-Demand Instances
- Reserved Instances
- Spot Instances
Per month, we have 750 hours for running
an instance. Comparatively, if there are 2 instances then the time will be
divided equally for both and as 750 hours will be completed or 12 months are
completed, we need to pay.
DISADVANTAGE:
- This is the most expensive instance.
- There is no discount and no commitment in On-Demand Instances.
- There is a possibility that this is not available for a huge number of services.
- If AWS infra is saturated then there is a possibility that we are not allowed to log in to our instance (Basically, it doesn’t happen because AWS provision a lot of hardware).
In this case, we can reserve the
instance for approx one to three years. We need to pay before starting the
instance for this and we need to provide the info that we want to run this
instance 24*7*365. If we choose Reserve instances, we can save approx 40% cost
for one year (here, the minimum reservation is for one year) and approx 60% cost for three years. If we extend this up to five
years, then we can save the cost up to 70%.
SCHEDULE INSTANCES:
Schedule Instance is a part of Reserved Instance. For example, if we reserve the instance for one year but our company is closed down on Saturday & Sunday and timings for Monday to Friday is from 8:00 am to 5:00 pm. In this case, the Reserved Instance will be expensive for us because we are paying for a full year. Here, Schedule Instance comes into the picture.
SCHEDULE INSTANCES:
Schedule Instance is a part of Reserved Instance. For example, if we reserve the instance for one year but our company is closed down on Saturday & Sunday and timings for Monday to Friday is from 8:00 am to 5:00 pm. In this case, the Reserved Instance will be expensive for us because we are paying for a full year. Here, Schedule Instance comes into the picture.
3. SPOT INSTANCES (good for fluctuating workload):
Spot Instances are free AWS
infrastructure which can be used for Happy Hours. At the time when AWS
infrastructure is free, then AWS release them as Happy Hours for us. Happy Hours
instances are not always available. We can get the instance with the discounted
amount up to 90%.
In this case, AWS releases an
amount for the instance, then everyone is going to bid for that. Whoever is
doing better bid, AWS will provide that instance to him.
ADVANTAGE:
Very high compute is available with 90% cheaper
cost.
DISADVANTAGE:
A. Spot Instances
3. INSTANCE TYPE
Cost also depends on the capacity of the hardware. So, we
must select the hardware flavor sincerely. There are many types of Instances we
have in AWS:
- General Purpose Workload (T & M): T for Tiny and M for Medium. CloudWatch is a feature, which tells us that there is an issue with performance or RAM etc. (In traditional data center we know this service as Nagios).
- Compute Optimized Instances (C): CPU% high
- Memory Optimized Instances (R): Ram% high
- Disk Optimized Instances (D): SSD / RAID, high Disk
- Graphical Optimized Instances (P): Graphics
- Extra Large Instance (X): CPU up to 128 & RAM 4TB
In 'C4 Large'; C is Instance Family, 4 is Instance
Generation and Large is Instance Size.
AMI
AMI (Amazon Machine Instance) is a readymade OS with apps, users and
readymade settings. We just need to map with EC2 service and launch the
instance. AMI is compatible with AWS infrastructure.
Amazon Marketplace is the location where we can get each
and everything related to AWS.
Q. How can we get our own PC to AWS?
A. AMI is Amazon readymade Operating System. But if we want
to use our own operating system in AWS, then first we need to use P2V and then
V2C.
- P2V: For this, we need to use a software named VMWare
Converter. Now our OS is converted into a vmdk file with extension .vmdk.
- V2C: There is no need for any software in V2C. For
this we just need to open VMWare > (VM should be shut down) > File > Export
to ovf. This will convert .vmdk file into .ovf.
- Now we need to send this file to the storage in AWS, which
is a bucket in S3.
- Taking a Virtual Machine from a data center to AWS S3
bucket is known as Migration.
- There is one more last step that we need to convert .ovf
file to AMI.
- Now, we have AMI but we need to download it on the hard disk
of EC2, which is known as EBS (Elastic Block Store).
- As AMI will expand on EBS, we can use this.
- To reach this instance we need internet which has Public
IP, Private IP, Net Card, Router, DNS. But as we are not expert in all this,
AWS is providing all of these things as VPC (Virtual Private Cloud). AWS
has created a default VPC in every region. We should never delete default VPC,
otherwise, we need to call to AWS and then we need to create this again.
- To protect our instance over the internet, we use firewalls. In AWS firewall
is known as SG (Security Group).
- We need to allow two ports: for Linux, we need to open port
22 for SSH and if this is a Windows, then we need to open port
number 3389 for rdp.
- We need to use a valid username and password. AWS
designed AMI images uses ec2-user as a username for Linux and Administrator as a username for Windows. Its password is inside the OS. But to get the password we need to
use a Public Key and a Private Key, which will be generated during the process
of instance creation. Public Key is always with AWS and Private key is always
with the user.
As we launch an instance, we need
to provide details on some fields:
There are some fields like 1. Choose AMI, 2. Choose Instance
Type, 3. Configure Instance, 4. Add Storage 5. Add Tags 6. Configure Security
Groups and 7. Review.
1.
Choose AMI:
We need to choose an AMI, which is a pre-build template. As we
are using a free account, we need to go only for Free Tier Images, otherwise, it
will be charged.
2.
Choose Instance Type:
There are a lot of options to select Instance Type. These Instances
are virtual servers that can run applications. Instance Type provides combinations
of CPU, memory, storage, and networking capacity, and give you the flexibility
to choose the appropriate mix of resources for your applications. So, we can
select any instance type as per our application requirement.
3.
Configure Instance:
Number of Instances: We can choose to launch more
than one instance at a time.
Purchasing option: We have the option to request Spot
Instances and specify the maximum price we are willing to pay per instance
hour. If our bid is higher than the current Spot Price, our Spot Instance will
be launched and also it will be charged at the current Spot Price.
Network: We can launch our instance by using AWS
default Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). We can create our own VPC and select our provided
IP address, subnets, route tables, and network gateways.
Subnet: A range of IP addresses in our VPC that can
be used to isolate different EC2 resources from each other or from the
Internet.
Auto-assign Public IP: We need to Enable it to make
our instance reachable from the Internet.
Placement group: We launch our instance in a
placement group to get the benefit from greater redundancy or higher networking
throughput.
Capacity Reservation: Capacity Reservations reserve
capacity for our EC2 instances in a specific Availability Zone. We can launch instances
into a Capacity Reservation if they have matching attributes (instance type, platform, and
Availability Zone), and available capacity.
IAM Role: *****
Shutdown behavior: Specify the instance behavior when
an OS-level shutdown is performed. Instances can be either terminated or
stopped.
Enable termination protection: We can protect
instances from being accidentally terminated.
Monitoring: Monitor, collect, and analyze instance
metrics through Amazon CloudWatch. The default is free, basic monitoring, where
data is available in 5-minute periods. You can enable detailed monitoring, where
data is available in 1-minute periods.
Tenancy: We can choose to run your instances on
physical servers fully dedicated for your use. We can go for Shared, Dedicated
Instance or Dedicated Host Tenancy models.
Elastic Inference: Elastic Inference provides cost
efficient hardware acceleration for all EC2 instance types.
T2/T3 Unlimited: Enabling T2/T3 Unlimited allows
applications to burst beyond the baseline for as long as needed at any time. If
the average CPU utilization of the instance is at or below the baseline, the
hourly instance price automatically covers all usage. Otherwise, all usage
above baseline is billed.
User Data: We can specify user data to configure an instance
or run a configuration script during launch.
4. Add
Storage:
We can see default Volume is selected as per our provided instance type. But we can add a new volume also by clicking on ADD NEW VOLUME. As we click on this we get a new volume having Volume Type 'EBS'.
5. Add
Tags:
Here we need to provide Name Tag because instance inside AWS
is identified by an instance ID. If we created 10-15 instances and we did not
provide any name tag then we will not be sure that which instance is doing
which job. This is not the hostname, this Name Tag is only to identify the
Instance inside AWS environment.
6.
Configure Security Group:
Here, by default SSH is selected, because for administration
in Linux we use SSH (port no. 22). Apart from SSH if we want to add another
rule, we need to click on 'Add Rule'. Now, either we can use an existing
Security Group or we can create a new Security Group. We can use this by choosing
the radio button in front of Assign a Security Group:
2. ( ) Select an existing security group. This will list all Existing Security Groups and we just need to click on selected one, having every rule provided in that Security Group > Next.







Good & detailed work Mr.Rastogi.
ReplyDeleteThanks Bikash :)
Deletemuch informative bro...Keep up the good work going.
ReplyDeletenice
ReplyDelete