We can host a website from S3 bucket in AWS. S3 is a highly scalable, extremely cheap and storage service. As it is a global service, so we do not bother to select any region. If we do not want to use any form, script or any type of input from users or we just want to provide information on our site, then, Static Web Hosting by using S3 bucket is really useful.
Generally, for a static website we need to have:
- Web Contents
- Web Location
- Public IP
- Domain Name Registration
- DNS Server
But if we go through AWS S3 bucket we need to perform:
- Register a Domain
- Create a Bucket
- Create a Bucket Policy (GetObject)
- Upload Files into the Newly Created Bucket
- Enable S3 Hosting
- Map IP to DNS via DNS Server
- Make a connection between Freenom and AWS
STEP 1: Register a Domain:
Visit a link https://www.freenom.com to register a free domain.
Find a free domain: Search a domain and purchase it as free
(in our practice we are using domain webshack.cf) ➔ Continue ➔ Checkout ➔ Login via using Gmail or Facebook OR click on login if you have an account ➔ Complete Order.
STEP 2: Create a Bucket:
AWS ➔ Services ➔ S3 ➔ Create Bucket ➔ Bucket name (it should be the same as the domain name): www.webshack.cf ➔ Next ➔ Uncheck all the boxes in 'Manage public access control lists (ACLs) for this bucket' to make bucket public ➔ Next ➔ Create Bucket.
Here, we can see that our bucket is created but access is not yet public (because of Implicit Deny).
STEP 3: Create a Bucket Policy:
AWS ➔ Services ➔ S3 ➔ Select Bucket: www.webshack.cf ➔ Permissions: copy Bucket ARN ➔ Bucket Policy ➔ Policy Generator ➔ Policy Type: S3 Bucket Policy ➔ Effect: Allow ➔ Principal: * ➔ Actions: GetObject ➔ ARN: (paste copied Bucket ARN) ➔ Add Statement ➔ Generate Policy ➔ Copy the code ➔ Paste it in Bucket policy editor with a
'/*' (ARN/*) ➔ Save.
If you want, you can use below mentioned Green colour code also:
Now the bucket has public access which AWS is notifying with orange indicator under Permissions.
If you want, you can use below mentioned Green colour code also:
{
"Id": "Policy1570222505991",
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Stmt1570222504297",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::bkt1adcvw/*",
"Principal": "*"
}
]
}
Now the bucket has public access which AWS is notifying with orange indicator under Permissions.
STEP 4: Upload Files into the newly created bucket
- Open notepad, put some contents in it and save it as 'index.html' again open another notepad window, put some contents in it and save it as error.html'.
- Go to the Bucket and upload files
in the bucket named www.webshack.cf:AWS ➔ Services ➔ S3 ➔ Select the bucket 'www.webshack.cf' ➔ Upload ➔ Add files ➔ Select files that you created ➔ Upload.
STEP 5: Enable S3 hosting:
AWS ➔ Services ➔ S3 ➔ Select the bucket
'www.webshack.cf' ➔ Properties ➔ Static Web Hosting ➔ [*] Use this
bucket to host a website ➔ Index document: index.html ➔ Error document:
error.html ➔ Save.
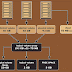
 |
| Fig: Static Web Hosting |
If we want, we can verify our site is working or not by clicking:
…Permissions ➔ Static web hosting ➔ Endpoint: URL ➔ Copy this URL and paste it on the browser to check if we get the access.
For example, in the above figure, we can see the Endpoint URL.
STEP 6: Map IP to DNS via DNS server:
AWS ➔ Services ➔ Route 53 (it’s a paid feature of AWS but if we clear it within 12 hours, there is no charge) ➔ DNS Management: Get Started Now ➔ Create Hosted Zone ➔ Create Hosted Zone ➔ Domain name: webshack.cf (do not provide www) ➔ Comment (provide purpose): Testing s3 web hosting ➔ Type: Public Hosted Zone ➔ Create.
Create Record Set ➔ Name: www (do not use dot after www) ➔ Type: A-IPv4 address ➔ Alias: Yes ➔ Alias Target: Select the Bucket
(if we are not getting our bucket name, then maybe the bucket name is wrong OR
static web hosting is disabled) ➔ Routing Policy: Simple ➔ Create.
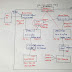
STEP 7: Make a connection between Freenom and AWS:
Login to freenom.com ➔ Services ➔ My Domains ➔ Click on Manage Domain in front of our domain 'webshack.cf' ➔ Management
Tools ➔ Name Servers ➔ [*] Use custom nameservers (enter below) ➔ (Here,
paste all four nameservers from our AWS window one by one WITHOUT DOT) ➔ Change
Nameservers.
 |
| Fig: Nameservers |
Now, our website is hosted, we need to verify this by using our
domain (www.webshack.cf) on the browser.
Open Web Browser ➔ Type www.webshack.cf ➔ If there is
no access, then we need to wait for some time. In some cases may take a couple
of moments to be online.
=============================================================
CLEANUP:
As we know, route 53 service is a paid service, if we use it beyond 12 hours. To avoid charges we need to delete our created 'Record Set' & 'Hosted Zone' and 'Disable Web Hosting':
1) Delete Record Set:
AWS ➔ Services ➔ Route53 ➔ Hosted Zones ➔ Select the Site ➔ Select the Record Set we want to delete ➔ Delete Record Set ➔ Confirm.
2) Remove Hosted Zone:
Go back to the Hosted Zones ➔ Select the site ➔ Delete Hosted Zone ➔ Confirm.3) Disable Static Website Hosting:
AWS ➔ Services ➔ Select Bucket ➔ Properties ➔ Static Web Hosting ➔ Disable Web Hosting ➔ Save.
4) Now, if there is no need of the bucket, we can also delete the bucket:
AWS ➔ Services ➔ S3 ➔ Select Bucket ➔ Delete ➔ Type the name of the bucket to confirm the deletion ➔ Confirm.
Enjoy!


Thanks much Divakar for posting this article....Worked like crisp!!!
ReplyDeleteThanks for sharing this informative article on Static Web Hosting Services in detail. If you have any requirement to Hire OVH Hosting Services for your web hosting service. Please visit us.
ReplyDelete