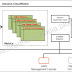
LDAP stands for 'Lightweight Access Protocol'. It’s a database which can be access over internet or intranet, whether you know domain or IP or not. LDAP database can access by many servers over a network. LDAP is also a database of
Users, Groups, Services and Resources, which provides a centralized
authentication service.
Before
starting an LDAP session, a client needs to connect to the server known as the
Directory System Agent, by default which
is set to TCP port 389. As connection is
established, the client and server exchange the packets of data.
What is SSL and TLS?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates are an integral part of website security. When you visit a website with SSL the site’s SSL certificate enables you to encrypt the data you send, such as credit card information, names or addresses so it can’t be accessed by hackers.
TLS (Transport Layer Security) is just an updated, more secure, version of SSL. This is also a cryptographic protocol like SSL that provides communications security over a computer network.
What is SSL and TLS?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates are an integral part of website security. When you visit a website with SSL the site’s SSL certificate enables you to encrypt the data you send, such as credit card information, names or addresses so it can’t be accessed by hackers.
TLS (Transport Layer Security) is just an updated, more secure, version of SSL. This is also a cryptographic protocol like SSL that provides communications security over a computer network.
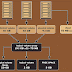
LDAP SERVER CONFIGURATION:
- Install openldap-servers package
- Check IP & hostname
- Modify olcDatabasev bdb.ldif file
- Modify olcDatabasev monitor.ldif file
- Create Database Cache
- Update Database
- Create certificate for TLS (Transport Layer Security)
- Provide ownership of ldap group to your certificate & test configuration
- Restart ldap
- Copy certificate to FTP document root
- Make soft link from FTP document root to HTTP document root
- Stop IPTables and disable Firewalls
- Install migrationtools package to migrate users
- Make changes in Migrate_common.ph
- Redirect output of ./migrate-base.pl to /root/base.ldif
- Create directory /home/guests
- Create Users
- Redirect these users from /etc/passwd to /root/users
- Redirect passwords for all these users from /etc/shadow to /root/passwords
- Redirect home groups for all these users from /etc/group to /root/groups
- Make changes in Migrate_password.ph
- Run script ./migrate_password.pl /root/users
- Run script ./migrate_group.pl /root/groups
- Update base.ldif, users.ldif and group.ldif files to LDAP Server
LDAP CLIENT CONFIGURATION:
- Check IP and hostname
- Access Ldap server & provide details
- Switch to ldapusers
ACCESS HOME DIRECTORY FROM LDAP SERVER:
- ACCESS LDAP SERVER and share home directory of ldap users via NFS server
- Restart NFS service
- ACCESS LDAP CLIENT and make auto-mounting
- Reload auto-mounting service
This tutorial describes how to install and configure an OpenLDAP server and an OpenLDAP client.
OPENLDAP SERVER:
Step1: Install openldap-servers
package.
# yum install openldap* -y
This will install four packages:
1. openldap-devel
2. openldap-servers
3. openldap-clients
4. cyrus-sasl-devel
# service slapd start
Step2: Check IP of PC on which
you want to install OpenLDAP. For example we can take 192.168.10.130
Step3. Check Hostname. Here, we
are using “ldap.example.com” and make an entry in /etc/hosts
# vi /etc/hosts
192.168.10.130 ldap.example.com ldap
We are done by installation. Now
we will configure LDAP Server by using ldif files under /etc/openldap/slapd.d
directory.
Step4: Modify olcDatabase
bdb.ldif file:
# vi /etc/openldap/slapd.d/cn=config/olcDatabase={1}bdb.ldif
<< Go to line number 5 and
provide your domain >>
olcSuffix: dc=example,dc=com
<< Go to line number 10 and
provide your domain >>
olcRootDN:
cn=Manager,dc=example,dc=com
NOTE: Do not set the cn of your
root user to "root" (cn=root,dc=acme,dc=com)
<<We must
make an entry for LDAP password. For this open another tab and use command
“slappasswd” to create ldap password. This will provide a string. Copy that
string and put in the last of this file. Also provide Certificate and
Certificate Key file path>>
olcRootPW:
{SSHA}uZLLxBTnVabGZCzBDulyvOJw/GauoADg
olcTLSCertificateFile: /etc/pki/tls/certs/example.pem
olcTLSCertificateFile: /etc/pki/tls/certs/example.pem
olcTLSCertificateKeyFile:
/etc/pki/tls/certs/examplekey.pem
:wq
Step5: Now we will provide
monitoring privileges:
# vi /etc/openldap/slapd.d/cn=config/olcDatabase\=\{2\}monitor.ldif
In line number 4 change “cn=Manager,dc=example,dc=com”
:wq
Step6: Now it’s time for the Database cache:
First copy DB_CONFIG.example file to /var/lib/ldap
# cp /usr/share/doc/openldap-servers-2.4.19/DB_CONFIG.example
/var/lib/ldap/DB_CONFIG
# chown -R ldap:ldap /var/lib/ldap/
Step7: Update Database:
# updatedb
Step8: Now we will setup a certificate for TLS. For this
first edit /etc/sysconfig/ldap:
# vi /etc/sysconfig/ldap
<<Go to Line Number 20 and change SLAPD_LDAPS from no to yes.>>
SLAPD_LDAPS=yes
SLAPD_LDAPS=yes
Now create a certificate
by using openssl command and active
it for
365 days:
# openssl req -new -x509 -nodes -out
/etc/pki/tls/certs/example.pem -keyout /etc/pki/tls/certs/examplekey.pem -days
365
<< openssl: crytographic toolkit for SSL & TLS n/w protocols >>
<< req: activates the parts of openssl that deals with certificate requests >>
<< -new: generate new request >>
<< -x509: certificate display and signing utility >>
<< -nodes: stores private key without protecting it with a passphrase >>
<< -out *.pem: stores certificate request in a file *.pem >>
<< -keyout *key.pem: stores private key in a file *key.pem >>
<< days: certificate activation days >>
<< openssl: crytographic toolkit for SSL & TLS n/w protocols >>
<< req: activates the parts of openssl that deals with certificate requests >>
<< -new: generate new request >>
<< -x509: certificate display and signing utility >>
<< -nodes: stores private key without protecting it with a passphrase >>
<< -out *.pem: stores certificate request in a file *.pem >>
<< -keyout *key.pem: stores private key in a file *key.pem >>
<< days: certificate activation days >>
This will ask for below mentioned details to create your
certificate, like:
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:IN
State or Province Name (full name) []:Maharashtra
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:Mumbai
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company
Ltd]:Mumbai.inc
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:IT
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname)
[]:ldap.example.com
Email Address []:root@ldap.example.com
You can verify both files:
# ll /etc/pki/tls/certs/example*
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1704 May 26 16:34
/etc/pki/tls/certs/examplekey.pem
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1448 May 26 16:34
/etc/pki/tls/certs/example.pem
Step9: Provide ownership of ldap group:
# chown -R root:ldap /etc/pki/tls/certs/example*
Verify:
# ll /etc/pki/tls/certs/example*
-rw-r--r--. 1 root ldap 1704 May 26 16:34
/etc/pki/tls/certs/examplekey.pem
-rw-r--r--. 1 root ldap 1448 May 26 16:34
/etc/pki/tls/certs/example.pem
Step10: Test your configuration:
# slaptest -u
config file testing succeeded
Step11: Restart LDAP service and make configuration on
# service slapd restart
# chkconfig slapd on
Step12: Now copy example.pem certificate to FTP default
document root:
# cp -rvf /etc/pki/tls/certs/example.pem /var/ftp/pub/
`/etc/pki/tls/certs/example.pem' ->
`/var/ftp/pub/example.pem'
# service vsftpd restart
# chkconfig vsftpd on
Step13: Create its soft link to default document root of
HTTP:
# ln -s /var/ftp/pub/ /var/www/html/
Verify:
# ll /var/www/html/
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 13 May 26 16:50 pub ->
/var/ftp/pub/
# Service httpd restart
# chkconfig httpd on
Step14: Stop iptables and disable Firewalls:
# service iptables stop
# chkconfig iptables off
# system-config-firewall
<<to disable Firewall>>
Step15: Organizations will often migrate to or from LDAP
engines, as they grow and acquire new companies and need to migrate users into
the same LDAP engine. So, now we will migrate the users:
# yum install migrationtools -y
Step16: Edit migrate_common.ph from directory:
# cd /usr/share/migrationtools
# vi migrate_common.ph
<<Change ou=Groups to cn=Groups at line number 61>>
$NAMINGCONTEXT{'group'} = "cn=Groups";
<<Change your Default DNS Domain at line number
71>>
$DEFAULT_MAIL_DOMAIN = "example.com";
<<Change Default Base at line number 74>>
$DEFAULT_BASE = "dc=example,dc=com";
<<Change Extended Schema at from 0 to 1 in line number
90>>
$EXTENDED_SCHEMA = 1;
:wq
:wq
Step17: Redirect migrate.base.pl to /root/base.ldif
./migrate_base.pl > /root/base.ldif
Step18: Now create a directory /home/guests for ldap users:
# mkdir /home/guests
Step19: Now, create users, here I am creating 5 users for
ldap;
# useradd -d
/home/guests/ldapuser1 ldapuser1
# useradd -d
/home/guests/ldapuser2 ldapuser2
# useradd -d
/home/guests/ldapuser3 ldapuser3
# useradd -d
/home/guests/ldapuser4 ldapuser4
# useradd -d
/home/guests/ldapuser5 ldapuser5
# passwd ldapuser1
# passwd ldapuser2
# passwd ldapuser3
# passwd ldapuser4
# passwd ldapuser5
Step20: Redirect all these users
from /etc/passwd to /root/users
# getent passwd | tail -n 5 >
/root/users
Step21: Redirect passwords for
all these users from /etc/shadow to /root/passwords
# getent shadow | tail -n 5 >
/root/passwords
Step22: Redirect home groups for
all these users from /etc/group to /root/groups
# getent group | tail -n 5 >
/root/groups
Step23: Now, make all these
changes in file “migrate_password.pl”
# vi migrate_password.pl
In Line number 188 replace
/etc/shadow to /root/passwords
Step24: Run the script command:
# ./migrate_passwd.pl /root/users
<<Here, you can check the
details of your users like uid, domain and cn etc>>
Redirect this output to ldif
file, because ldap understands configuration file ended with *.ldif.
# ./migrate_passwd.pl /root/users
> /root/users.ldif
Step25: Run the script command:
# ./migrate_group.pl /root/groups
<<Here, you can check group
details>>
Redirect this output to ldif
file, because ldap understands configuration file ended with *.ldif.
# ./migrate_group.pl /root/groups > /root/groups.ldif
Now we have three ldif files in
/root location
# ll /root/*.ldif
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2061 May
26 17:20 /root/base.ldif
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 690 May 26 17:48 /root/groups.ldif
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2750 May
26 17:45 /root/users.ldif
Step26: Finally, we will update
these files to LDAP Server:
Upload base.ldif:
# ldapadd -x -W -D
”cn=Manager,dc=example,dc=com” -f /root/base.ldif
Upload users.ldif:
# ldapadd -x -W -D
”cn=Manager,dc=example,dc=com” -f /root/users.ldif
Now upload groups.ldif:
# ldapadd -x -W -D
”cn=Manager,dc=example,dc=com” -f /root/groups.ldif
<<You can check your
ldap>>
# ldapsearch -x -b
"dc=example,dc=com"
<<LDAP SERVER IS CONFIGURED
NOW>>
OPENLDAP CLIENT:
Go to client machine in your
network to use LDAP Server and its users.
Step1: Check IP of PC from which
you want to access ldap server. For example we can take 192.168.10.133
Step2: Hostname must be different
from the hostname of server, like;
# hostname
redhat.panacia.com
Step3: Verify user:
# su – ldapuser1
su: user ldapuser1 does not exist
Step4: Finally access ldap server
by using one of below commands:
# system-config-authentication
OR
# authconfig -gtk
This will open a window. In
Identity and Aithentication tab:
1. User account Database: LDAP
2. LDAP Search Base DN: dc=example,dc=com
3. LDAP Server: ldap://ldap.example.com
4. Check Check box in TLS to encrypt selections
5. Click on Download CA Certificate and provide
Certificate URL: http://ldap.example.com/pub/example.pem
<<you
can check certificate by using same url in browser>>
6. Authentication Method: LDAP Password
6. Authentication Method: LDAP Password
7. Finally hit on Apply, this will show output:
Starting sssd: [
OK ]
Step5: You can check all five
users by:
# getent passwd ldapuser1
ldapuser1:*:502:502::/home/guests/ldapuser1:/bin/bash
getent passwd ldapuser2
ldapuser2:*:503:503::/home/guests/ldapuser2:/bin/bash
# getent passwd ldapuser3
ldapuser3:*:504:504::/home/guests/ldapuser3:/bin/bash
# getent passwd ldapuser4
ldapuser4:*:505:505::/home/guests/ldapuser4:/bin/bash
# getent passwd ldapuser5
ldapuser5:*:506:506::/home/guests/ldapuser5:/bin/bash
Step6: Now, switch to your
ldapuser
# su - ldapuser1
su: warning: cannot change
directory to /home/guests/ldapuser1: No such file or directory
-bash-4.1$
Here, you can see that your
ldapuser1 can login but it's not have home directory yet. So, if you want to
access home directory from ldap server; AGAIN GO BACK TO LDAP SERVER and share
home directories via NFS server:
Step7: Install NFS server;
# yum install nfs* -y
# service nfs start
Step8: Share home directory and
restart NFS service:
# vi /etc/exports
/home/guests 192.168.10.0/255.255.255.0(rw,sync)
# Service nfs restart
# chkconfig nfs on
<<Verify mounting>>
# showmount -e ldap.example.com
Export list for ldap.example.com:
/home/guests 192.168.10.0/255.255.255.0
Step9: GO BACK TO LDAP CLIENT and make
auto-mounting:
<<Go to auto.master file
and make entry>>
# vi /etc/auto.master
/home/guests /etc/auto.guests
<<Go to auto.guests file
and make entry>>
# vi /etc/auto.guests
* -rw
ldap.example.com:/home/guests/&
Step10: Reload autofs service:
# service autofs reload
Step11: Now again access ldap
server by user ldapuser1:
# su - ldapuser1
[ldapuser1@redhat ~]$
# su - ldapuser2
[ldapuser2@redhat ~]$
# su - ldapuser3
[ldapuser3@redhat ~]$
# su - ldapuser4
[ldapuser4@redhat ~]$
# su - ldapuser5
[ldapuser5@redhat ~]$


No comments:
Post a Comment